This is a quick summary on Falsy and Nullish values in JavaScript. JavaScript has 8 falsy values, and 2 nullish values. The two nullish values are also falsy, but the rest of the falsy values are not nullish.
Falsy Values
A falsy value is something that is considered as false when used in a boolean context. JavaScript uses Type Coercion to convert non-boolean values in boolean contexts (such as a conditional, or a loop) into boolean form. There are 8 falsy values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
false | The keyword false |
0 | Number 0 |
-0 | Negative number 0 |
0n | 0 in BigInt |
‘’, “” | Empty string |
null | Primitive null – no value |
undefined | Primitive undefined |
NaN | Not a Number |
Nullish Values
The two primitives null and undefined are known as nullish. Put simply, it means that they don’t have any value. They get converted to false via Type Coercion in a boolean context.
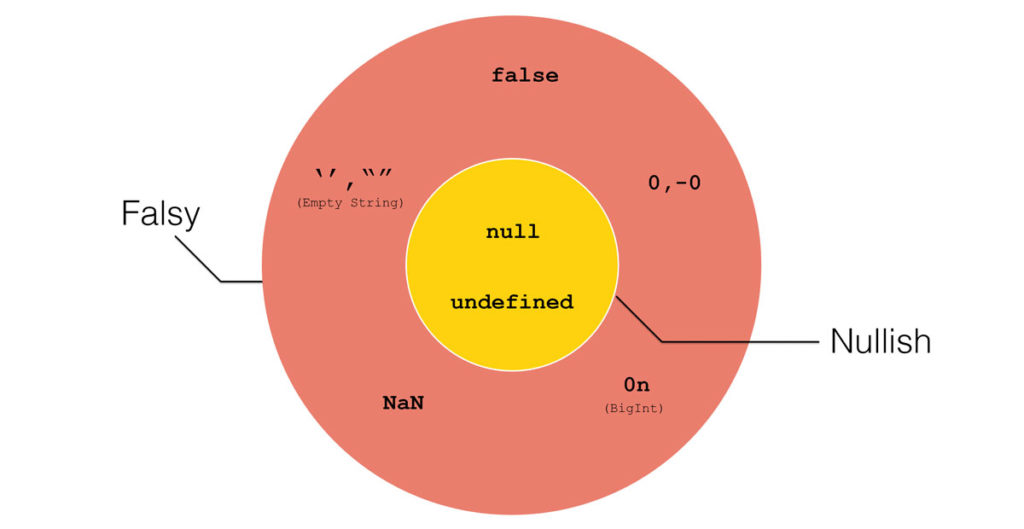
By above definitions, we see that nullish values are also falsy.
0 vs null vs undefined
Fundamentally being a numerical value, 0 is used to denote that a countable thing has none of its kind. It can be used with arithmetic operations.
The special primitive value null represents the intentional absence of a value in any context, not just numerically. It needs to be explicitly set by a developer. Zero says a countable thing is empty, whereas null says the property or variable is known and exists, but is intentionally holding no value. Oddly, the type of null, when checked with typeof null, is shown to be object.
Similarly, undefined is a primitive value, but it is also a JavaScript type. It represents that a property or variable has not yet been assigned a value, intentionally or not. It is the default result when you try to access a property that does not exist.